Biomedical imaging
Biomedical imaging is an interdisciplinary area that combines medicine, engineering, physics, mathematics and computational technologies. The main objective, in the clinical context, is to devise and develop new non-invasive imaging systems and methods (hardware and software) for the visualization of living beings, mainly humans. Imaging modalities of interest include magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), planar X-rays, computed tomography (CT) and ultrasound, among others.
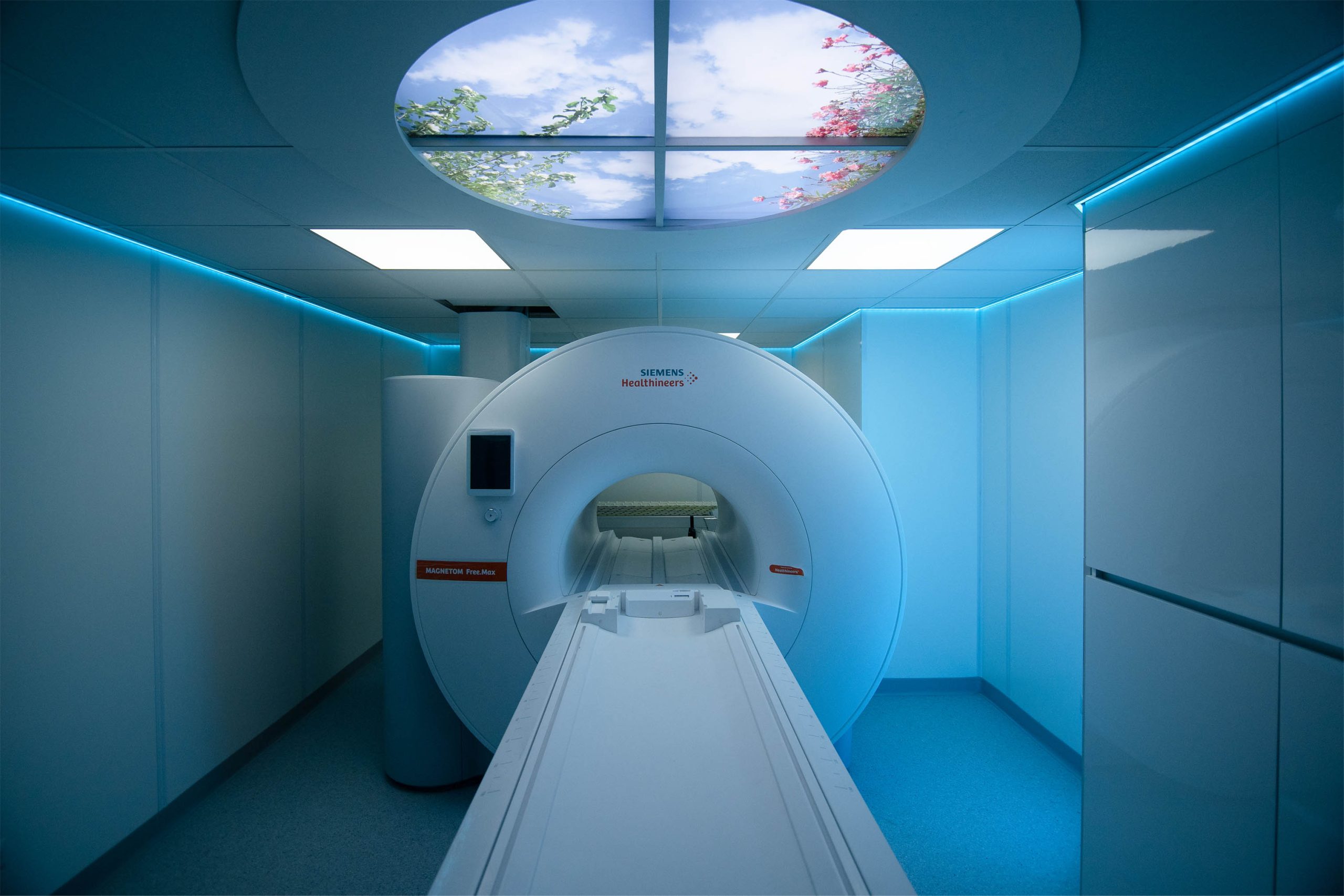
The institute's biomedical imaging research focuses on the development and application of new image acquisition, reconstruction, processing and modeling technologies for medicine and life sciences. More recently, research also includes the development of low-field (0.55T) MRI methods and ultra-low-field (0.05T) point-of-care MRI scanners, as well as the development and use of artificial intelligence methods throughout the imaging process to make imaging more efficient, affordable, quantitative and user-friendly. Clinical applications include imaging of the heart, lungs, liver, and brain and the use of imaging for early diagnosis, risk stratification, treatment planning and monitoring, and prognosis.
Other fields of research include imaging-based research and associated treatment of emotional disorders, neurorehabilitation of movement pathologies and brain connectomics.
Fondos adjudicados
1
Basal Center (PI)
2
Large equipment grant (CI)
1
Basal Center (PI)
Biomechanics and Quantitative Physiology
Large equipment grant (CI)